What Tissue Forms Blood Cells . Web the cellular elements—referred to as the formed elements—include red blood cells (rbcs), white blood cells (wbcs), and cell fragments called. However, 2 types of white blood cells—t. Web red blood cells, most white blood cells, and platelets are produced in the bone marrow. Web blood cell formation, continuous process by which the cellular constituents of blood are replenished as. Web the volume percentage of all blood cells in the whole blood is about 45% of adults (hematocrit). Web there are three main blood cell types: Identify the composition of blood plasma, including its most important solutes and plasma proteins. Why is it considered to be fluid connective tissue. White (leukocytes), red (erythrocytes), and platelets. The rest consists of liquid plasma (e.g. Web discuss the unique physical characteristics of blood. Web blood is fluid connective tissue that circulates throughout the body.
from encyclopedia.pub
Why is it considered to be fluid connective tissue. However, 2 types of white blood cells—t. Web blood is fluid connective tissue that circulates throughout the body. Web the volume percentage of all blood cells in the whole blood is about 45% of adults (hematocrit). Web blood cell formation, continuous process by which the cellular constituents of blood are replenished as. The rest consists of liquid plasma (e.g. Web red blood cells, most white blood cells, and platelets are produced in the bone marrow. Web discuss the unique physical characteristics of blood. Web the cellular elements—referred to as the formed elements—include red blood cells (rbcs), white blood cells (wbcs), and cell fragments called. White (leukocytes), red (erythrocytes), and platelets.
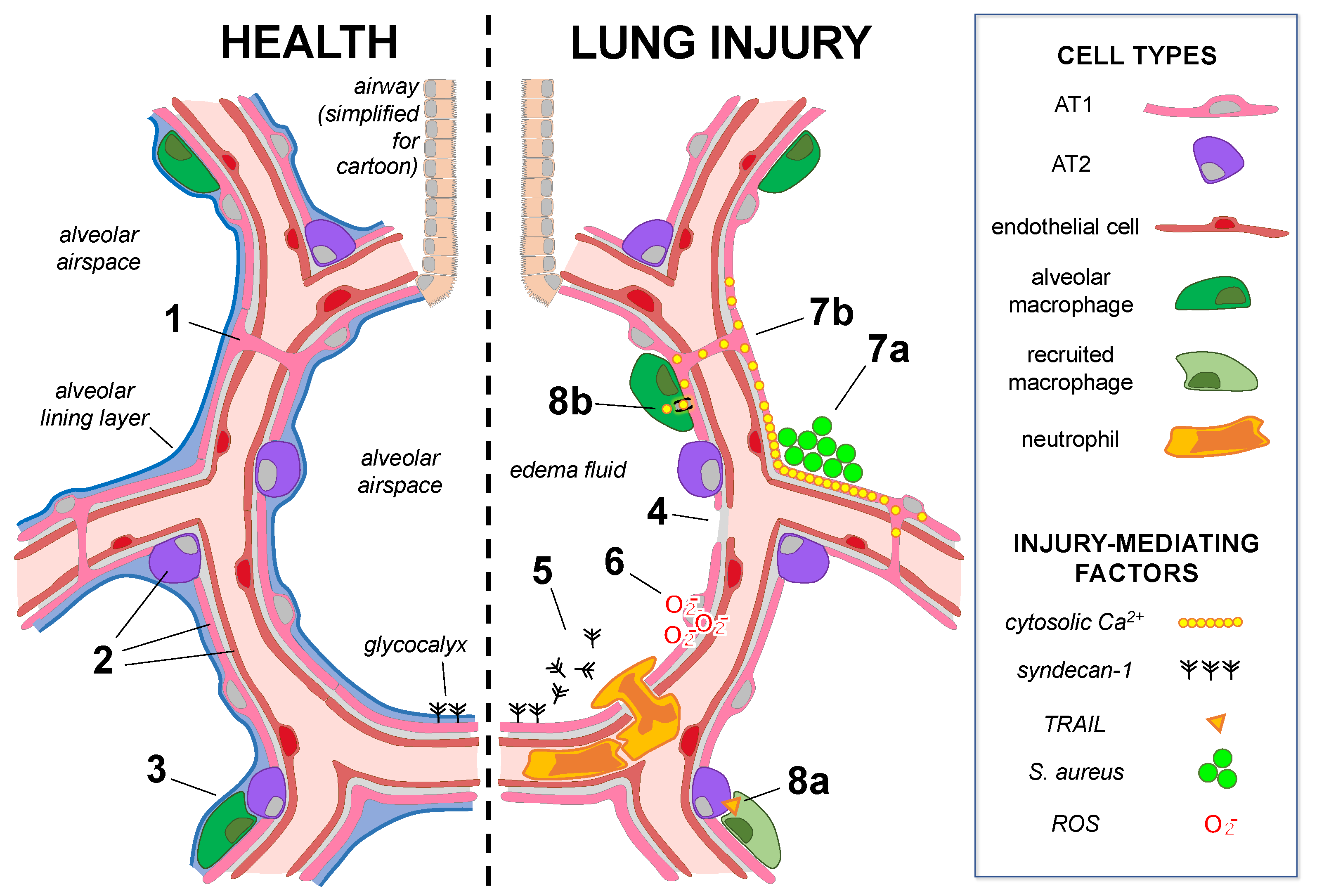
The Alveolar Epithelium at Homeostasis Encyclopedia MDPI
What Tissue Forms Blood Cells Web the cellular elements—referred to as the formed elements—include red blood cells (rbcs), white blood cells (wbcs), and cell fragments called. Identify the composition of blood plasma, including its most important solutes and plasma proteins. Web red blood cells, most white blood cells, and platelets are produced in the bone marrow. Why is it considered to be fluid connective tissue. Web there are three main blood cell types: Web the cellular elements—referred to as the formed elements—include red blood cells (rbcs), white blood cells (wbcs), and cell fragments called. Web blood is fluid connective tissue that circulates throughout the body. Web discuss the unique physical characteristics of blood. Web the volume percentage of all blood cells in the whole blood is about 45% of adults (hematocrit). However, 2 types of white blood cells—t. Web blood cell formation, continuous process by which the cellular constituents of blood are replenished as. White (leukocytes), red (erythrocytes), and platelets. The rest consists of liquid plasma (e.g.
From www.britannica.com
White blood cell Definition & Function Britannica What Tissue Forms Blood Cells Web blood cell formation, continuous process by which the cellular constituents of blood are replenished as. Web the volume percentage of all blood cells in the whole blood is about 45% of adults (hematocrit). White (leukocytes), red (erythrocytes), and platelets. Web there are three main blood cell types: Why is it considered to be fluid connective tissue. However, 2 types. What Tissue Forms Blood Cells.
From www.animalia-life.club
White Blood Cell Parts What Tissue Forms Blood Cells Web blood is fluid connective tissue that circulates throughout the body. Web blood cell formation, continuous process by which the cellular constituents of blood are replenished as. Web there are three main blood cell types: The rest consists of liquid plasma (e.g. Web discuss the unique physical characteristics of blood. White (leukocytes), red (erythrocytes), and platelets. Identify the composition of. What Tissue Forms Blood Cells.
From www.dreamstime.com
All Blood Cells Scientific Overview Vector Image Stock Vector What Tissue Forms Blood Cells Identify the composition of blood plasma, including its most important solutes and plasma proteins. White (leukocytes), red (erythrocytes), and platelets. Web the cellular elements—referred to as the formed elements—include red blood cells (rbcs), white blood cells (wbcs), and cell fragments called. Web blood is fluid connective tissue that circulates throughout the body. Why is it considered to be fluid connective. What Tissue Forms Blood Cells.
From humanbio.org
2b2 Muscle Structure HumanBio What Tissue Forms Blood Cells Web there are three main blood cell types: Web the volume percentage of all blood cells in the whole blood is about 45% of adults (hematocrit). The rest consists of liquid plasma (e.g. White (leukocytes), red (erythrocytes), and platelets. Web red blood cells, most white blood cells, and platelets are produced in the bone marrow. Web discuss the unique physical. What Tissue Forms Blood Cells.
From printablevialetto0t.z21.web.core.windows.net
The 4 Types Of Tissue What Tissue Forms Blood Cells However, 2 types of white blood cells—t. Web there are three main blood cell types: Web red blood cells, most white blood cells, and platelets are produced in the bone marrow. White (leukocytes), red (erythrocytes), and platelets. Web the cellular elements—referred to as the formed elements—include red blood cells (rbcs), white blood cells (wbcs), and cell fragments called. Identify the. What Tissue Forms Blood Cells.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
Types of Tissues Anatomy and Physiology I What Tissue Forms Blood Cells Web the cellular elements—referred to as the formed elements—include red blood cells (rbcs), white blood cells (wbcs), and cell fragments called. Web the volume percentage of all blood cells in the whole blood is about 45% of adults (hematocrit). Web blood cell formation, continuous process by which the cellular constituents of blood are replenished as. Identify the composition of blood. What Tissue Forms Blood Cells.
From blog.cellsignal.com
Immunology What Cells Have a Myeloid Lineage and How Are they Identified? What Tissue Forms Blood Cells However, 2 types of white blood cells—t. Why is it considered to be fluid connective tissue. Identify the composition of blood plasma, including its most important solutes and plasma proteins. Web there are three main blood cell types: White (leukocytes), red (erythrocytes), and platelets. Web red blood cells, most white blood cells, and platelets are produced in the bone marrow.. What Tissue Forms Blood Cells.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT HUMAN ANATOMY PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID9469608 What Tissue Forms Blood Cells Web blood is fluid connective tissue that circulates throughout the body. The rest consists of liquid plasma (e.g. Web there are three main blood cell types: Web discuss the unique physical characteristics of blood. Web the volume percentage of all blood cells in the whole blood is about 45% of adults (hematocrit). Web the cellular elements—referred to as the formed. What Tissue Forms Blood Cells.
From ceynsmqh.blob.core.windows.net
Tissue Form Blood Cells at Ricky Perry blog What Tissue Forms Blood Cells Web blood is fluid connective tissue that circulates throughout the body. The rest consists of liquid plasma (e.g. Web blood cell formation, continuous process by which the cellular constituents of blood are replenished as. Web red blood cells, most white blood cells, and platelets are produced in the bone marrow. Web the volume percentage of all blood cells in the. What Tissue Forms Blood Cells.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Human Primary Endothelial Cells A Model for Blood Vessel What Tissue Forms Blood Cells Identify the composition of blood plasma, including its most important solutes and plasma proteins. Web blood is fluid connective tissue that circulates throughout the body. Why is it considered to be fluid connective tissue. Web the volume percentage of all blood cells in the whole blood is about 45% of adults (hematocrit). Web the cellular elements—referred to as the formed. What Tissue Forms Blood Cells.
From www.dreamstime.com
Blood cells stock image. Image of bloodcell, experiment 8898869 What Tissue Forms Blood Cells Identify the composition of blood plasma, including its most important solutes and plasma proteins. Web the volume percentage of all blood cells in the whole blood is about 45% of adults (hematocrit). However, 2 types of white blood cells—t. White (leukocytes), red (erythrocytes), and platelets. Web there are three main blood cell types: The rest consists of liquid plasma (e.g.. What Tissue Forms Blood Cells.
From doctorstotrust.com
PAUL MASON c1 HEART ATTACK …cholesterol in PLAQUES NOT FROM LDL What Tissue Forms Blood Cells Web the volume percentage of all blood cells in the whole blood is about 45% of adults (hematocrit). Web there are three main blood cell types: Web the cellular elements—referred to as the formed elements—include red blood cells (rbcs), white blood cells (wbcs), and cell fragments called. However, 2 types of white blood cells—t. Why is it considered to be. What Tissue Forms Blood Cells.
From www.thesciencehive.co.uk
Transport in humans (GCSE) — the science hive What Tissue Forms Blood Cells White (leukocytes), red (erythrocytes), and platelets. Web the cellular elements—referred to as the formed elements—include red blood cells (rbcs), white blood cells (wbcs), and cell fragments called. The rest consists of liquid plasma (e.g. Identify the composition of blood plasma, including its most important solutes and plasma proteins. Web blood is fluid connective tissue that circulates throughout the body. Web. What Tissue Forms Blood Cells.
From labpedia.net
Anemia Part 9 Sideroblastic Anemia, and Anemia Due To Chronic What Tissue Forms Blood Cells Web discuss the unique physical characteristics of blood. The rest consists of liquid plasma (e.g. Web there are three main blood cell types: Web blood cell formation, continuous process by which the cellular constituents of blood are replenished as. Why is it considered to be fluid connective tissue. Web the volume percentage of all blood cells in the whole blood. What Tissue Forms Blood Cells.
From indiatook.com
रुधिर की आंतरिक संरचना ( Structure of Blood in Hindi ) What Tissue Forms Blood Cells Web red blood cells, most white blood cells, and platelets are produced in the bone marrow. Identify the composition of blood plasma, including its most important solutes and plasma proteins. Web blood is fluid connective tissue that circulates throughout the body. Web there are three main blood cell types: Web discuss the unique physical characteristics of blood. Why is it. What Tissue Forms Blood Cells.
From ie.pinterest.com
Connective Tissues Loose connective tissue, Body tissues, Tissue biology What Tissue Forms Blood Cells Web the cellular elements—referred to as the formed elements—include red blood cells (rbcs), white blood cells (wbcs), and cell fragments called. Web there are three main blood cell types: Web blood is fluid connective tissue that circulates throughout the body. Web the volume percentage of all blood cells in the whole blood is about 45% of adults (hematocrit). Why is. What Tissue Forms Blood Cells.
From www.chegg.com
Solved Any tissues that exist in layers and form linings or What Tissue Forms Blood Cells Why is it considered to be fluid connective tissue. Web blood cell formation, continuous process by which the cellular constituents of blood are replenished as. The rest consists of liquid plasma (e.g. Web red blood cells, most white blood cells, and platelets are produced in the bone marrow. White (leukocytes), red (erythrocytes), and platelets. However, 2 types of white blood. What Tissue Forms Blood Cells.
From knowt.com
A & P 1 Lab Exercise 2 Organ Systems Overview Flashcards Knowt What Tissue Forms Blood Cells Web the volume percentage of all blood cells in the whole blood is about 45% of adults (hematocrit). Web the cellular elements—referred to as the formed elements—include red blood cells (rbcs), white blood cells (wbcs), and cell fragments called. Web there are three main blood cell types: Identify the composition of blood plasma, including its most important solutes and plasma. What Tissue Forms Blood Cells.